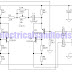
The operation of the converter is based on the weighted adding and transferring of the analogue input levels and the digital output levels. It consists of comparators and resistors. In theory, the number of bits is unlimited, but each bit needs a comparator and several coupling resistors. The diagram shows a 4-bit version. The value of the resistors must meet the following criteria:
- R1:R2 = 1:2;
- R3:R4:R5 = 1:2:4;
- R6:R7:R8:R9 = 1:2:4:8.
The linearity of the converter depends on the degree of precision of the value of the resistors with respect to the resolution of the converter, and on the accuracy of the threshold voltage of the comparators. This threshold level must be equal, or nearly so, to half the supply voltage. Moreover, the comparators must have as low an output resistance as possible and as high an input resistance with respect to the load resistors as feasible. Any deviation from these requirements affects the linearity of the converter adversely.
Circuit diagram:

Source :www.extremecircuits.net