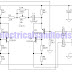
This power supply uses an LM317J adjustable regulator and an MJ2955 pass transistor. Ql and U2 as well as Ul should be heats inked. A suitable heat-sink would typically be 4` 4` 1` fins, extruded type, because up to 65 W dissipation can occur. R8 and R9 should be 1% types or selected from 5% film types with an accurate ohmmeter. Capacitors are disc ceramic except for those with polarity marked, which are electrolytic. D1, D2—1-A, 100-PIV rectifier diode. DS1—Red LED. F1 —1,5-A, 3AG fuse in chassis-mount holder. J1, J2—Standard five-way binding post, one red, one black. M1—Milli-ammeter, 0-1 mA dc. Q1—NPN power transistor MJ2955 (Radio Shack) or equiv device with a + 70-V, 10-A, 150-W rating in a -204 case. R1, R2, R7—5-W wire-wound resistor. See Notes 3 and 4 for source, or, use 17 inches of no. 28 enam wire, single-layer wound, on a 10-KOhmhm, 1-W carbon-composition resistor for R1 and R7. For R2, use 36 inches of no. 30 enam wire on a 10-KOhmhm, 1-W carbon composition resistor (scramble wound). R-4—Panel-mount, 5-kfi, 2-W or 5-W potentiometer, carbon or wire wound (See Note 8). R8, R9—See text. 51—SPST toggle switch. 52—DPDT toggle or rotary wafer switch. T1—25.2-V, 2.75-A power transformer (see text). U1—6-A, 200 PIV bridge rectifier with heat sink. See text. U2—LM317T +1.25- to 30-V, 1.5-A 7-220 regulator. Use an LM317HVK (T0-204 case) for dc output voltage greater than 40. See text.
2.5A-1.25 To 25V Regulated Power Supply Circuit Diagram








 The LEDs are arranged so that when the polarity across the circuit is one way only one LED will light and when the polarity reverses the other LED will light, therefore when no transistor is connected to the tester the LEDs will alternately flash. The IC2 outputs are also connected to resistors R4 and R5 with the junction of these two resistors connected to the base of the transistor being tested.
The LEDs are arranged so that when the polarity across the circuit is one way only one LED will light and when the polarity reverses the other LED will light, therefore when no transistor is connected to the tester the LEDs will alternately flash. The IC2 outputs are also connected to resistors R4 and R5 with the junction of these two resistors connected to the base of the transistor being tested.